Bellman Equation
We now introduce the Bellman equation, a mathematical tool for analyzing state values.
In a nutshell 简而言之, the Bellman equation is a set of linear equations that describe the relationships between the values of all the states. State values
We next derive the Bellman equation. First, note that
where
The two terms in (2.4) are analyzed below.
可以分为两项,第一项是现在,第二项是加上折扣因子的未来
The first term,
策略
Here,
The second term,
状态
的discounted return的期望是 state value - 下一步为
的概率, 可以由策略 下采取动作 到达状态 的概率
The above derivation uses the fact that
Substituting (2.5)-(2.6) into (2.4) yields
This equation is the Bellman equation, which characterizes the relationships of state values. It is a fundamental tool for designing and analyzing reinforcement learning algorithms.
The Bellman equation seems complex at first glance. In fact, it has a clear structure.
Some remarks are given below.
and are unknown state values to be calculated. It may be confusing to beginners how to calculate the unknown given that it relies on another unknown . It must be noted that the Bellman equation refers to a set of linear equations for all states rather than a single equation. If we put these equations together, it becomes clear how to calculate all the state values. Details will be given in Section 2.7. is a given policy. Since state values can be used to evaluate a policy, solving the state values from the Bellman equation is a policy evaluation process, which is an important process in many reinforcement learning algorithms, as we will see later in the book. and represent the system model. We will first show how to calculate the state values with this model in Section 2.7, and then show how to do that without the model by using model-free algorithms later in this book.
In addition to the expression in (2.7), readers may also encounter other expressions of the Bellman equation in the literature. We next introduce two equivalent expressions.
First, it follows from the law of total probability that
Then, equation (2.7) can be rewritten as
Second, the reward
2.5 Examples for illustrating the Bellman equation
We next use two examples to demonstrate how to write out the Bellman equation and calculate the state values step by step. Readers are advised to carefully go through the examples to gain a better understanding of the Bellman equation.
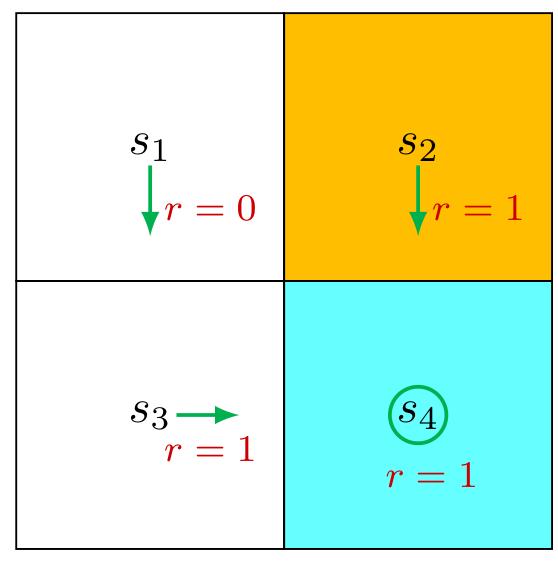
Consider the first example shown in Figure 2.4, where the policy is deterministic. We next write out the Bellman equation and then solve the state values from it.
First, consider state
Interestingly, although the expression of the Bellman equation in (2.7) seems complex, the expression for this specific state is very simple.
Similarly, it can be obtained that
We can solve the state values from these equations. Since the equations are simple, we can manually solve them. More complicated equations can be solved by the algorithms presented in Section 2.7. Here, the state values can be solved as
Furthermore, if we set
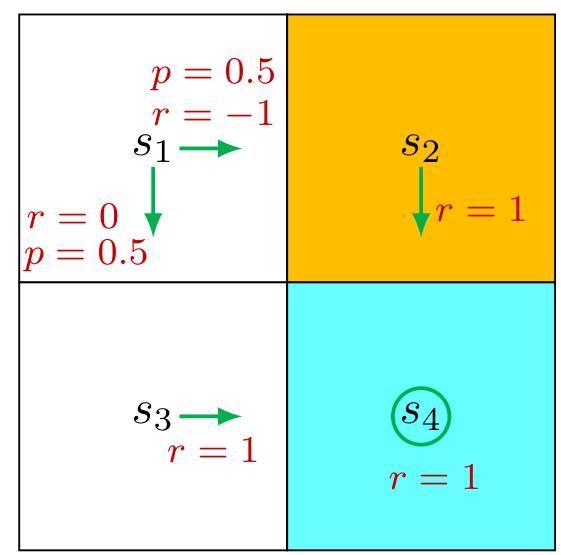
Consider the second example shown in Figure 2.5, where the policy is stochastic. We next write out the Bellman equation and then solve the state values from it.
In state
Similarly, it can be obtained that
The state values can be solved from the above equations. Since the equations are
simple, we can solve the state values manually and obtain
Furthermore, if we set
If we compare the state values of the two policies in the above examples, it can be seen that
which indicates that the policy in Figure 2.4 is better because it has greater state values. This mathematical conclusion is consistent with the intuition that the first policy is better because it can avoid entering the forbidden area when the agent starts from